How to Transition from Waterfall to Agile
Published:
Updated:
Introduction to Transitioning from Waterfall to Agile
The shift from Waterfall to Agile methodologies is becoming increasingly common as organizations seek to improve flexibility, collaboration, and time-to-market. While Waterfall has been the traditional approach for decades—especially in industries like construction and manufacturing—it often struggles to meet the demands of today’s fast-paced, dynamic environments. Agile, on the other hand, offers a more iterative and adaptive approach, making it ideal for projects where requirements evolve over time.
However, transitioning from Waterfall to Agile is not just about adopting new tools or processes—it requires a fundamental shift in mindset and culture. Teams must embrace:
- Collaboration: Cross-functional teamwork and shared ownership.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular retrospectives and process optimizations.
- Customer-Centricity: Frequent feedback loops to ensure product-market fit.
In this guide, we’ll explore how to transition from Waterfall to Agile effectively. We’ll cover:
- The key differences between Waterfall and Agile
- A step-by-step roadmap for the transition
- Common challenges and how to overcome them
Whether you’re a project manager, team leader, or executive driving the change, this post will equip you with the knowledge to make the shift seamless.
For a broader overview of Agile frameworks, check out our pillar post: The Ultimate Guide to Agile Project Management Methodology.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the differences : Agile is iterative and flexible, while Waterfall is linear and rigid.
- Start small : Pilot Agile practices on a single project or team before scaling.
- Use tools and templates : Leverage tools like Jira, Trello, and Asana to streamline workflows.
- Monitor progress : Track metrics and hold regular retrospectives to ensure continuous improvement.
Key Differences Between Waterfall and Agile
Understanding the differences between Waterfall and Agile is essential for a successful transition. Below is a comparison of the two methodologies:
| Aspect | Waterfall | Agile |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Linear and sequential | Iterative and incremental |
| Flexibility | Rigid; changes are costly | Adaptable; welcomes changes |
| Delivery | Single delivery at the end | Frequent, incremental deliveries |
| Team Structure | Hierarchical and role-specific | Cross-functional and self-organizing |
| Customer Involvement | Limited to initial phases | Continuous feedback throughout the process |
Why Transition to Agile?
- Faster Time to Market: Agile delivers usable increments early, allowing businesses to capitalize on opportunities sooner.
- Improved Collaboration: Agile fosters collaboration between cross-functional teams and stakeholders.
- Higher Adaptability: Agile thrives in dynamic environments where requirements evolve over time.
- Continuous Feedback: Agile encourages continuous feedback from stakeholders, ensuring that the final product meets their needs.
Step-by-Step Roadmap for Transitioning from Waterfall to Agile
Transitioning from Waterfall to Agile requires careful planning and execution. Below is a step-by-step roadmap to guide your organization through the process:
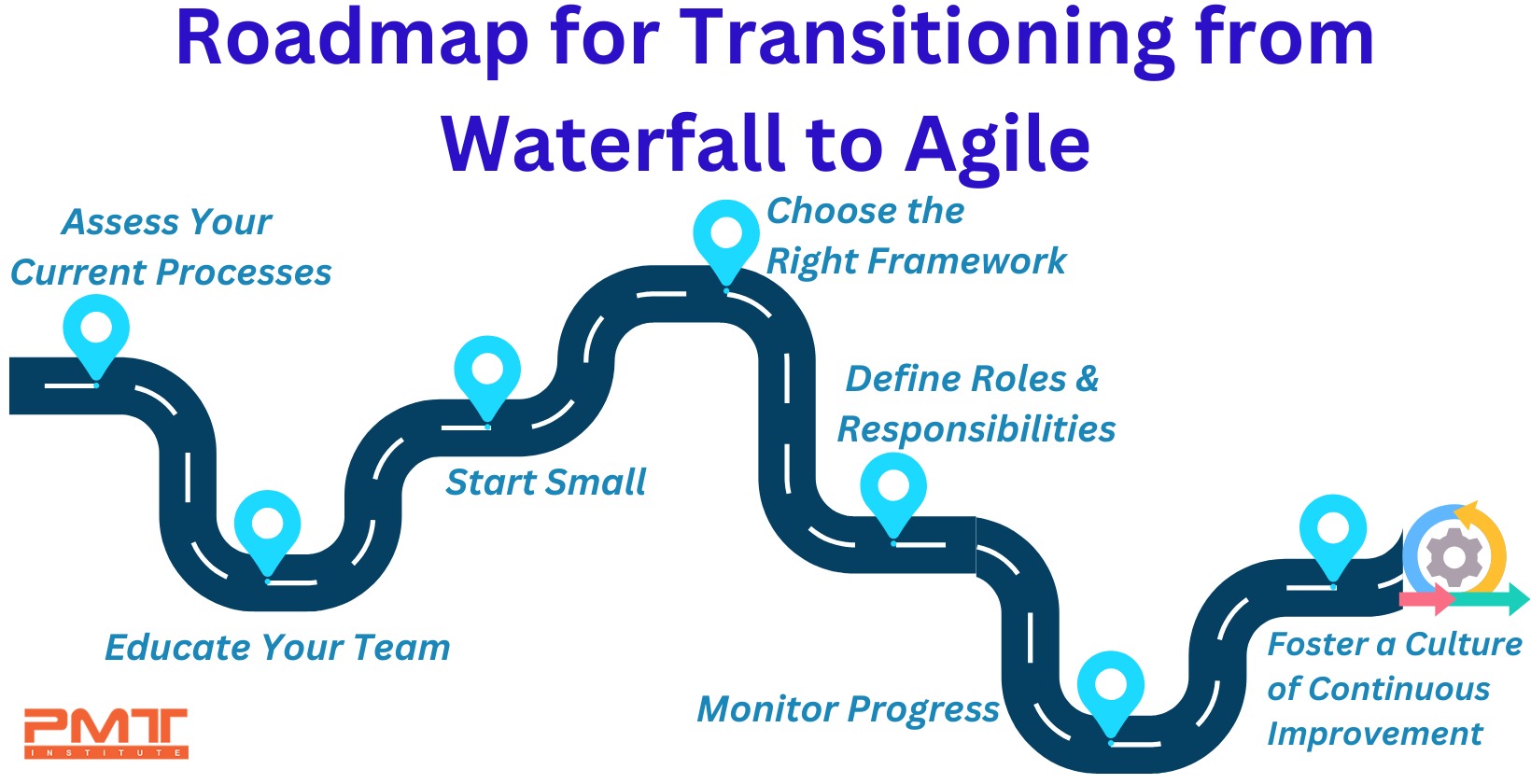
Step 1: Assess Your Current Processes
- Conduct a thorough analysis of your existing Waterfall processes to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
- Determine which aspects of Waterfall can be retained and which need to be replaced with Agile practices.
Step 2: Educate Your Team
- Provide training sessions or workshops to introduce key Agile concepts like Scrum, Kanban, and the Agile Manifesto.
- Consider hiring an Agile Coach to guide your team through the transition.
Step 3: Start Small
- Begin with a pilot project or a single team to test Agile practices without overwhelming the organization.
- Choose a project that is relatively low-risk and has a clear scope.
Step 4: Choose the Right Framework
Select an Agile framework that aligns with your team’s needs and the nature of your project:
- Scrum: Ideal for teams working on complex projects with rapidly changing requirements.
- Kanban: Better suited for teams managing ongoing, unpredictable workloads.
- SAFe: Designed for large enterprises that need to scale Agile across multiple teams and departments.
Step 5: Define Roles and Responsibilities
Clearly define roles within your Agile team to avoid confusion and ensure accountability:
- Product Owner: Responsible for defining the product vision and prioritizing the backlog.
- Scrum Master: Facilitates the Scrum process, removes obstacles, and ensures that the team adheres to Agile principles.
- Development Team: A cross-functional group of professionals who deliver the product increment at the end of each sprint.
Step 6: Monitor Progress
- Use metrics like velocity, cycle time, and throughput to track performance.
- Regular retrospectives will help you identify areas for improvement and ensure that your team is continuously refining its processes.
Step 7: Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement
- Encourage a culture of continuous improvement by regularly reflecting on what went well, what could be improved, and how to implement those improvements in future sprints.
Common Challenges in Transitioning from Waterfall to Agile
Transitioning from Waterfall to Agile is not without its challenges. Below are some common obstacles organizations face and strategies to overcome them:
1. Resistance to Change
Challenge: Employees accustomed to Waterfall may resist Agile practices, fearing increased workload or uncertainty.
Solution: Clearly communicate the benefits of Agile, such as flexibility, faster delivery, and improved collaboration. Involve teams in the transition process and address their concerns through open discussions.
2. Lack of Training
Challenge: Without proper training, teams may struggle to adopt Agile principles, leading to inconsistent implementation.
Solution: Invest in training sessions and provide access to Agile resources. Consider hiring an Agile Coach to mentor teams and ensure a smooth transition.
3. Unclear Roles and Responsibilities
Challenge: Ambiguity in roles can create confusion, reducing team efficiency.
Solution: Clearly define Agile roles:
- Product Owner: Manages the product backlog and prioritizes work.
- Scrum Master: Facilitates Agile ceremonies and removes blockers.
- Development Team: A cross-functional team responsible for delivering product increments.
4. Overloading Teams with Too Many Changes
Challenge: Implementing too many Agile practices at once can overwhelm teams.
Solution: Start small with a pilot project or one team. Gradually introduce Agile frameworks (Scrum, Kanban, SAFe) and scale practices across the organization.
5. Misaligned Expectations
Challenge: Stakeholders may expect immediate results from Agile adoption.
Solution: Set realistic expectations and emphasize that Agile is an iterative journey, not a quick fix. Use Agile metrics to showcase progress over time.
Tools to Support the Transition
Several tools can help support the transition from Waterfall to Agile by streamlining workflows and improving collaboration. Below are some of the top tools and templates to ease the transition:
Agile Project Management Tools
| Tool | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Jira | Agile backlogs, sprints, retrospectives | Supports Scrum & Kanban, backlog management, sprint tracking |
| Trello | Visualizing workflows | Kanban boards, drag-and-drop task management, customizable lists |
| Asana | Task and backlog management | Sprint planning, backlog grooming, task dependencies |
| Monday.com | Automating Agile workflows | Custom boards, automation features, real-time collaboration |
Agile Templates to Simplify the Transition
Using templates can help teams adapt to Agile more effectively. Below are some essential templates for a smooth transition:
- Sprint Planning Template: Helps teams organize and prioritize tasks for each sprint.
- Retrospective Meeting Template: Captures what went well, what could be improved, and action items for the next sprint.
- Backlog Prioritization Template: Assists Product Owners in prioritizing user stories based on business value and effort.
Real-World Examples of Successful Transitions
Many organizations have successfully transitioned from Waterfall to Agile, improving flexibility, collaboration, and delivery speed. Below are some notable case studies of companies that have embraced Agile methodologies.
Example 1: IBM
| Challenge | IBM struggled with rigid Waterfall processes that slowed down innovation and reduced adaptability. |
|---|---|
| Solution | IBM adopted Agile methodologies across its software development teams, focusing on Scrum and SAFe. |
| Outcome | Improved collaboration, faster time to market, and higher-quality products. |
Example 2: Spotify
| Challenge | As a rapidly growing company, Spotify needed a way to scale Agile practices across multiple teams without reducing autonomy. |
|---|---|
| Solution | Spotify implemented a unique Agile framework called the "Spotify Model,” which emphasizes squad-based autonomy, tribes, and collaborative guilds. |
| Outcome | Increased innovation, faster delivery cycles, and improved employee satisfaction. |
Example 3: Capital One
| Challenge | Capital One faced challenges with lengthy Waterfall cycles that delayed product releases and made responding to customer needs difficult. |
|---|---|
| Solution | The company transitioned to Agile, focusing on Lean-Agile principles and SAFe to improve efficiency. |
| Outcome | Enhanced customer experience, streamlined operations, and significantly reduced time to market. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Transitioning from Waterfall to Agile
Below are some common questions about transitioning from Waterfall to Agile, along with clear and practical answers.
Answer:
Resistance to change is often the biggest challenge in transitioning from Waterfall to Agile. Many employees are accustomed to traditional workflows and may feel uncertain about new processes. To overcome this:
- Provide Agile training and coaching to help teams understand the benefits.
- Start with a pilot project to demonstrate Agile’s effectiveness.
- Involve leadership in fostering an Agile mindset.
Answer:
The transition timeline depends on factors such as company size, industry, and team experience. However, most organizations take 6–12 months to fully adopt Agile practices. Here’s a general breakdown:
- 0–3 months: Initial Agile training, leadership buy-in, and pilot projects.
- 3–6 months: Scaling Agile across multiple teams, refining processes.
- 6–12 months: Full adoption, continuous improvement, and advanced Agile practices.
Answer:
Yes, some organizations use a hybrid approach, combining Agile and Waterfall methodologies. This is often referred to as “Agile-Waterfall Hybrid” or "Wagile". It works well in scenarios where:
- Regulatory requirements demand structured documentation (Waterfall).
- Development teams need flexibility and iterative feedback (Agile).
- Large projects with different phases benefit from structured planning (Waterfall) while maintaining agility in execution (Agile).
By integrating both methodologies, companies can tailor their processes to fit their needs.
Conclusion & Next Steps
Transitioning from Waterfall to Agile is a significant shift that requires changes in mindset, processes, and team collaboration. While the transition may present challenges, the benefits—such as improved adaptability, faster delivery cycles, and increased stakeholder engagement—make it well worth the effort.
By following a structured roadmap, investing in training, and leveraging the right Agile tools, organizations can successfully embrace Agile methodologies and continuously improve their workflows.
Next Steps to Ensure a Smooth Transition
- Start Small: Begin with a pilot project to test Agile methodologies before rolling them out across the organization.
- Educate Your Team: Provide training on Agile principles, frameworks (Scrum, Kanban, SAFe), and best practices.
- Use the Right Tools: Leverage Agile project management tools like Jira, Trello, or Monday.com to facilitate the transition.
- Monitor & Adjust: Regularly review team progress, hold retrospectives, and continuously refine your Agile practices.
- Seek Expert Guidance: Consider hiring an Agile Coach or engaging with an Agile consultancy to accelerate the transition.
Embracing Agile is not a one-time switch but an ongoing journey of continuous improvement. Organizations that commit to Agile principles will see long-term benefits in productivity, innovation, and customer satisfaction.

