Schedule Performance Index (SPI) - PMP Exam
Published:
Updated:
For the success of any project, it is essential that the project stays on track. However, as a project manager, you must determine whether the project is on schedule. But the main question is how you can tell if the project is right on track or falling behind.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding SPI: The Schedule Performance Index (SPI) measures project schedule efficiency by comparing earned value (EV) to planned value (PV).
- Calculation Formula: SPI is calculated using the formula SPI = EV / PV. An SPI of 1.0 means the project is on schedule.
- Interpreting SPI: An SPI greater than 1.0 indicates the project is ahead of schedule, while an SPI less than 1.0 suggests it is behind schedule.
- Practical Example: For instance, if EV is $200,000 and PV is $250,000, the SPI would be 0.8, indicating the project is 80% on schedule.
- Advantages and Disadvantages: SPI provides a clear view of schedule performance but does not account for project quality or cost variances.
In order to determine it, the project management professionals use the Schedule Performance Index (SPI) to determine the project's efficiency and effectiveness. In this article, Project Management Training Institute will explain all the things about SPI and how you can use it to measure the project's progress.
Related topic: If you want to check out our resource for Cost Performance Index (CPI), please click on the link.
Schedule Performance Index (SPI) is used for performance measurement by expert project managers both in private and public (government) industry. Combined with other EVM measures it is a powerful way to understand and forecast project performance.
Introduction to the Schedule Performance Index (SPI)
SPI, or Schedule Performance Index, can be defined as a project management tool used to measure the efficiency of a project's schedule. It determines how much progress has been made and whether the project is right on schedule.
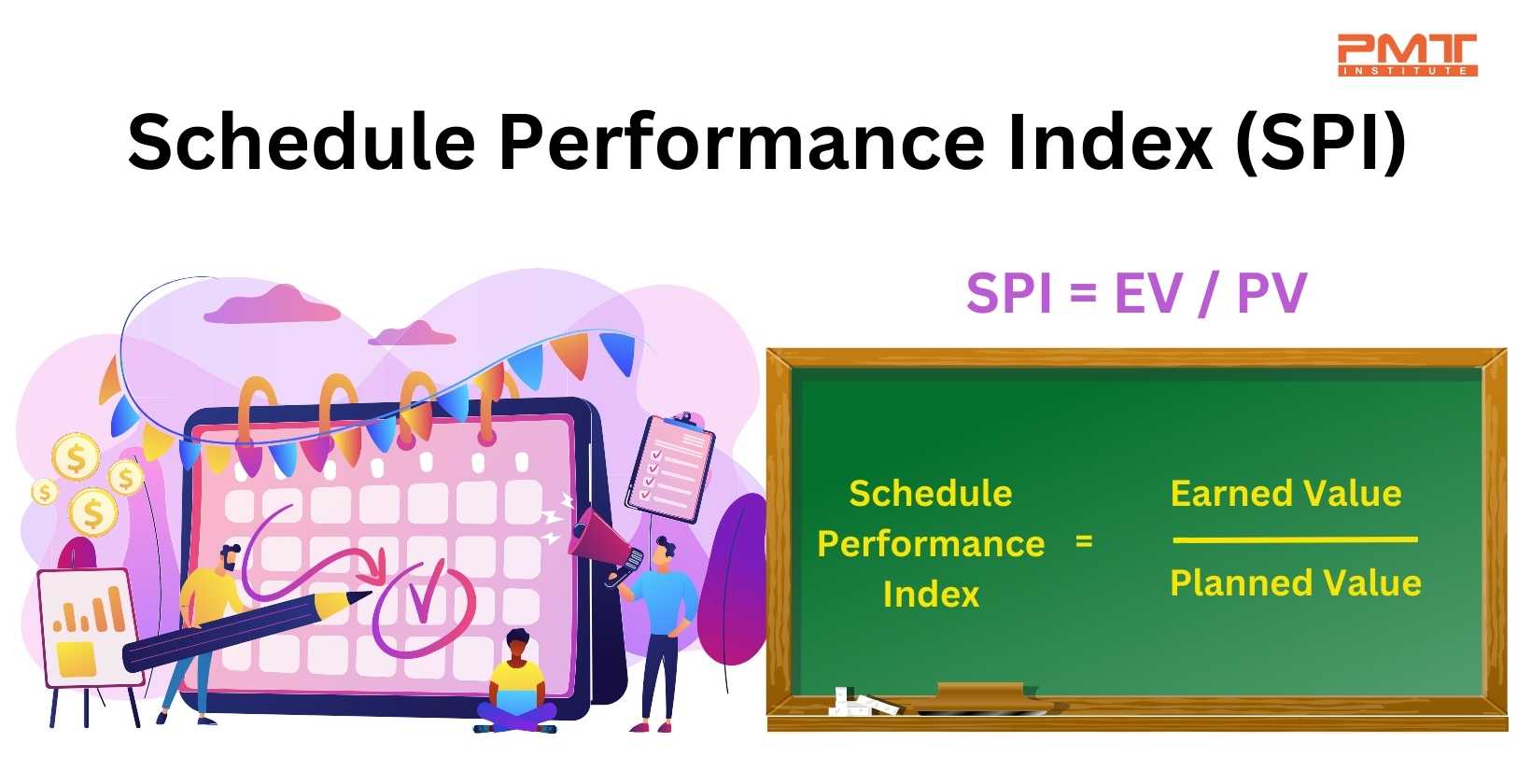
It compares how much progress a project team has made on the schedule compared to how much progress it was expected to make. The Schedule Performance Index is a ratio calculated using the following formula.
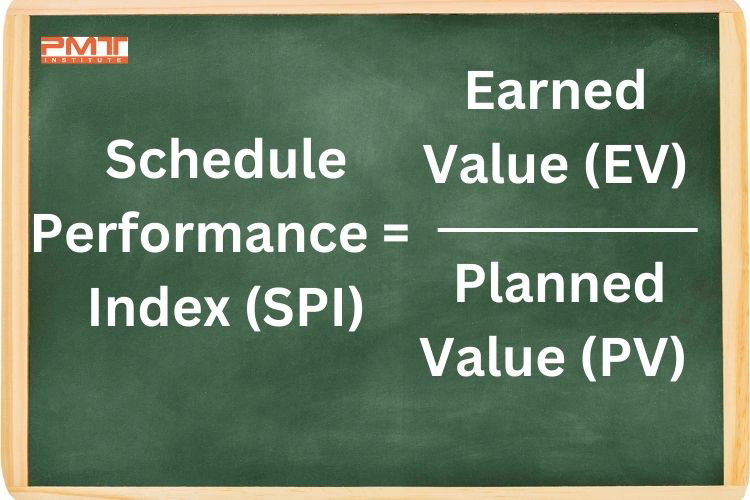
SPI = EV/ PV
In this formula, EV represents Earned Value, which measures the amount of work completed on the project. This EV is calculated by multiplying the percentage of work the project's budget has completed. On the other hand, the PV represents Planned Value, which measures the amount of work planned to be completed at a given time. You can calculate it by multiplying the percentage of the budget that was planned to be spent at a given point in time by the budget of the project.
How to Calculate the Schedule Performance Index (SPI)
In order to calculate the SPI, you have to find out the Earned Value (EV) and the Planned Value (PV) for the project at a given point in time. For calculating Earned Value, you have to multiply the percentage of work that the budget of the project has completed. Whereas, to calculate Planned Value, you have to multiply the percentage of the budget that was planned to be spent at a given point in time by the budget of the project.
SPI Calculation Example
Calculating the Schedule Performance Index (SPI) involves comparing the earned value (EV) with the planned value (PV) of a project. For example, if a project has an earned value of $200,000 and a planned value of $250,000, the SPI is calculated as:
SPI =EV/PV? = 200,000/250,000 =0.8
This SPI of 0.8 indicates the project is progressing at 80% of the planned schedule, suggesting it is behind schedule and requires adjustments to meet deadlines.
To help you understand how you can use this formula, we’ll share an example with you.
Suppose you are managing a project that has a budget of $500,000. After the first month, 30% of the work has been completed, and 30% of the budget has been spent on the project. The EV of the project would be $150,000 (30% X $500,000). The PV of the project after the first month would also be $150,000 (30% X $500,000).
We have both Earned Value and Planned Value of the project. Now it is very simple to calculate the SPI for the project at the end of the first month, which is as follows. SPI = $150,000/$150,000 = 1.0
This means the project is right on schedule and expected to be completed within the projected time frame.
Interpreting the Schedule Performance Index (SPI)
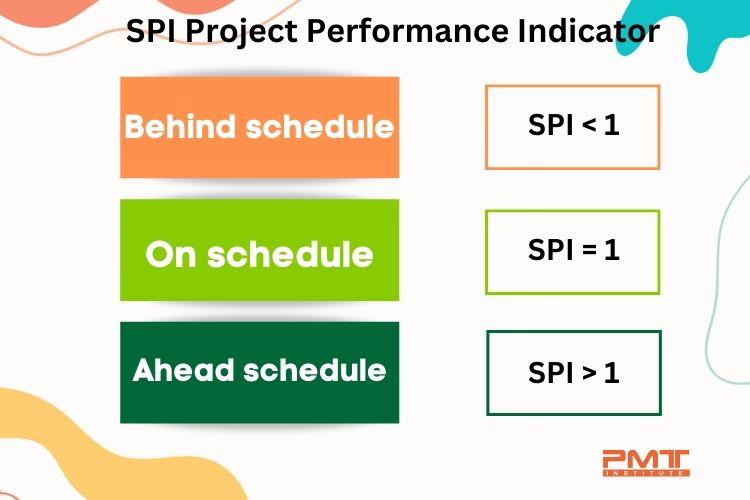
Once you have calculated the SPI, you will know whether a project is on schedule, ahead of schedule, or behind schedule. If you get an SPI of 1, the project is on schedule. If you get an SPI of greater than 1, it means the project is ahead of schedule. While an SPI of less than 1 indicates, the project is behind schedule.
However, the SPI only tells you about the project's scheduled performance at a given point in time. It does not consider any changes or updates to the project schedule that may have occurred since the project began. Therefore, it is important to regularly monitor and update the SPI to ensure that it accurately reflects the project's current state.
In addition, it is important to consider other factors that may impact the SPI, such as changes in the project scope, budget, or resources. These factors can affect the Earned Value and Planned Value calculations that can directly impact the SPI calculation.
What does a SPI of 0.8 mean?
An SPI of 0.8 shows that the project is completing work at 80% of the planned rate, indicating a delay in the schedule.
What does a SPI of 0.5 mean?
A SPI of 0.5 signifies significant delays, with the project progressing at only half the planned pace.
What does an SPI of 0.9 mean?
An SPI of 0.9 suggests the project is slightly behind schedule, operating at 90% of the planned pace.
What does a SPI of 1.2 mean?
A SPI of 1.2 indicates the project is ahead of schedule, completing 20% more work than planned.
What does an SPI of greater than 1.0 mean?
An SPI greater than 1.0 indicates that the project is ahead of schedule, and performing better than planned.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Schedule Performance Index (SPI)
Although SPI itself is a useful tool to provide “the rate at which the project is progressing”, it gets enhanced dramatically when combined with Cost Performance Index (CPI) and Budget At Completion (BAC) to understand the past and predict future. Let’s learn about the pros and cons of this measure.
The SPI is a useful tool for project managers as they can measure the project's progress and whether the project is set to be completed within the time. To tell you more about this SPI, we have shared some advantages and disadvantages of using SPI in project management. But first, let's discuss the advantages.
Advantages
There are several advantages to using the SPI in project management:
- Quick and accurate assessment: The SPI provides a quick and accurate assessment of a project's schedule performance at a given point in time.
- Early identification of issues: By regularly calculating and monitoring the SPI, project managers can identify any problems or issues with the project schedule early on and take corrective action to get the project back on track.
- Determination of project status: The SPI can be used to determine whether a project is on schedule, ahead of schedule, or behind schedule. This allows project managers to adjust the project plan accordingly.
- Simple and easy to understand: The SPI is a simple and easy-to-understand tool that can be used by project managers and stakeholders to assess the project's schedule performance quickly.
- Integration with other tools: The SPI can be used in conjunction with other project management tools and techniques, such as earned value analysis, to get a complete picture of the project's progress and performance.
Disadvantages
There are also some disadvantages to using the SPI:
- Limited scope: The SPI only considers the progress of the project schedule and does not take into account other factors that may impact the project, such as changes in the project scope, budget, or resources.
- Incorrect results due to poor estimation: The SPI may be affected by issues such as poor estimation or unrealistic project plans, which can lead to inaccurate results.
- Requires standard calculation and monitoring: To get the most out of the SPI, it must be regularly calculated and monitored. This can be time-consuming and requires a certain level of expertise to interpret the results properly.
- Please don't take any changes into account: SPI only measures the project's schedule performance at a given point in time, as it does not take into account any changes or updates to the project schedule.
Examples of SPI Calculation in Project Management
Following are some examples of how the SPI can be used in project management:
Example 1: Imagine a project with 10 walls. Each wall costs $15,000 and takes 1 month to complete. If at the end of the fourth month, the project accomplished to complete three walls, the project would have earned three walls worth of work meaning the Earned Value or EV is $15,000 x 3 = $45,000. However, the estimated completion in four months would have been four walls so the Planned Value or PV would be $15,000 x 4 = $60,000. So, applying the formula for SPI.
SPI = EV/PV =$45,000/$60,000 = ¾ = 0.75
This implies the project is progressing at 75% efficiency. A simpler way to look at it would be to say the project is completing three walls when it should have completed four walls during this project period.
Example 2: A project manager monitors the progress of a construction project. At the end of the first month, the project team completed 10% of the work and spent 20% of the budget. The project manager calculates the SPI for the project and finds that it is 0.5. This SPI of 0.5 indicates that the project is behind schedule, so the project manager must investigate the cause of the delay and take some action to get the project back on track.
Example 3: Take another example of a project manager monitoring a research project's progress. After the first month, the project team completed 40% of the work and spent 20% of the total allocated budget. The project manager calculates the SPI for the project and finds that it is 2.0.
This means that the project is ahead of the schedule and expected to be completed before the given timeline. After knowing that the project is ahead of schedule, the project manager will be able to make some adjustments to the project plan and can take advantage to use the extra time and resources available more effectively.
Best Practices for Using Schedule Performance Index (SPI)
To get the most out of the Schedule Performance Index (SPI) in project management, it is important to follow these best practices:
- Regularly calculate and monitor the SPI: To ensure that the SPI accurately reflects the project's current state, it is important to calculate and monitor it regularly. This allows project managers to identify any deviations from the project plan and take corrective action to get the project back on track.
- Use the SPI in conjunction with other project management tools: The SPI is just one tool in a project manager's toolkit. Project managers can get a complete picture of the project's progress and performance by using it in conjunction with other project management tools and techniques, such as earned value analysis.
- Please take into account changes to the project: It is important to consider any changes or updates to the project schedule, scope, budget, or resources that may affect the SPI calculations. This ensures that the SPI accurately reflects the current state of the project.
- Use the SPI to identify problems and take corrective action: By regularly calculating and monitoring the SPI, project managers can identify any problems or issues with the project schedule and take corrective action to get the project right back on track.
- Communicate the results to stakeholders: It is important to communicate the results of the SPI to all relevant stakeholders, including the project team, project sponsors, and customers. This ensures that everyone is aware of the progress of the project and any potential issues that may need to be addressed.
Summary
To sum it up, the Schedule Performance Index (SPI) is a valuable tool for project managers as it can help in measuring the efficiency of the project's schedule. This simple and easy-to-use tool in project management helps identify problems and make accurate assessments of a project's schedule at a given time. By following the best practices of using SPI, project managers can effectively use the SPI to keep the projects right on track.


