PMP Risk Assessment Matrix: How to Create Probability and Impact Matrix in Project Management
Published:
Updated:

In the fast-paced and ever-changing landscape of project management, risks are an inevitable part of any undertaking. Identifying and managing these risks are essential to ensuring the successful completion of projects. Risk probability and impact assessment, along with the probability and impact matrix, are powerful tools that enable project managers to understand, prioritize, and mitigate potential threats effectively. We will delve into the concepts of risk probability, impact assessment, and the probability and impact matrix in this blog.
Key Takeaways
Understanding Risk Assessment Matrix: The Probability and Impact Matrix is essential for prioritizing project risks based on their likelihood and potential impact.
Creating the Matrix: Learn step-by-step instructions on developing an effective risk assessment matrix tailored to your project needs.
Risk Mitigation Strategies: Explore various techniques and examples of risk mitigation strategies to minimize the impact of identified risks.
Evaluating Effectiveness: Understand the importance of continuously evaluating the effectiveness of your risk mitigation strategies to ensure project success.
Enhancing Project Management Skills: Improve your project management capabilities by mastering the creation and use of the Probability and Impact Matrix.
Understanding Risk Probability
What is Risk Probability?
In the realm of project management, risk probability refers to the likelihood of a specific risk event occurring during the course of a project. As no project is entirely free from uncertainties, accurately assessing the probability of risks is crucial for focusing on the most relevant and potentially harmful ones. You must learn risk probability from a Project Risk Management Course to equip yourself.
Factors Influencing Risk Probability
Several factors influence the assessment of risk probability. These include historical data and trends from similar projects, expert judgment from experienced team members, the complexity of the project itself, and external factors such as economic conditions, political stability, and environmental impacts.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Probability Assessment
There are two main approaches to assessing risk probability. The first is a quantitative assessment, which involves assigning numerical probabilities to risks based on historical data and statistical analysis. The second is a qualitative assessment, where risks are categorized as low, medium, or high probability based on expert judgment and subjective evaluation.
Impact Assessment of Risks
What is Risk Impact?
Risk impact refers to the potential consequences or effects that may result from the occurrence of a specific risk event. Understanding the potential impacts is critical for effective risk mitigation and resource allocation.
Evaluating Risk Impact
To comprehensively assess risk impact, project managers must consider various dimensions, including:
-
Financial impact
The potential costs and financial losses associated with a risk event.
-
Schedule impact
The potential time delays and disruptions to the project timeline.
-
Reputational impact
The effect on the project"s reputation and the organization"s brand.
-
Safety and environmental impact
The potential harm to employees, stakeholders, or the environment.
-
Stakeholder impact
The effect on key stakeholders and their interests.
Understanding the risk probability and impact matrix is crucial for effectively assessing and prioritizing project risks. To dive deeper into comprehensive risk management strategies and learn how to implement these processes throughout your projects, explore our detailed article on risk management processes. This resource provides a thorough exploration of identifying, analyzing, responding to, and monitoring risks, ensuring you have the tools to manage uncertainties effectively and protect your project outcomes.
Measuring Quantitative Impact
Quantitative impact assessment involves assigning monetary values to potential impacts or calculating the potential time delays caused by specific risk events. Additionally, project managers can quantify reputational or stakeholder impacts by conducting surveys or assessments to gauge perceptions and sentiment.
Likelihood and Impact Matrix
The Likelihood and Impact Matrix is a crucial tool in project risk management. It helps project managers assess and prioritize risks based on their probability of occurrence and potential impact on the project. Here’s a detailed look at its components and usage:
Likelihood
- Likelihood refers to the probability of a risk event occurring. It is usually expressed in qualitative terms (e.g., high, medium, low) or quantitative percentages.
- Assessment:
- High: Greater than 70% chance of occurring.
- Medium: 30%-70% chance of occurring.
- Low: Less than 30% chance of occurring.
- Factors Affecting Likelihood:
- Historical data and past project experiences.
- Expert judgment and analysis.
- Environmental and operational conditions.
Matrix Construction
Steps
- Identify Risks: List all potential risks identified during the risk assessment phase.
- Determine Likelihood and Impact: Assess each risk based on its probability and impact.
- Plot Risks on the Matrix: Use a 5x5 grid (or similar) to plot risks, with likelihood on one axis and impact on the other.
- Prioritize Risks: Focus on high-likelihood, high-impact risks for immediate attention.
-
Divide risk probability and impact into categories (e.g., low, medium, high) to establish a clear scale.
-
Create a grid with probability on one axis and impact on the other, resulting in a matrix layout.
-
Assign risk ratings to cells based on the intersection of probability and impact categories.
-
High-risk areas (high probability and high impact) require immediate attention and detailed risk response plans.
-
Moderate-risk areas (medium probability and impact) warrant proactive planning and risk mitigation strategies.
-
Low-risk areas (low probability and impact) can be monitored with less urgency but should not be disregarded entirely.
-
Avoidance:
- Technique: Eliminate the risk entirely by changing project plans.
- Example: Choosing a proven technology over an untested one to avoid technical failures.
-
Reduction:
- Technique: Implement measures to decrease the likelihood or impact of the risk.
- Example: Providing additional training to team members to reduce the risk of errors.
-
Transference:
- Technique: Shift the risk to a third party.
- Example: Purchasing insurance or outsourcing risky project components.
-
Acceptance:
- Technique: Acknowledge the risk and prepare to manage its impact.
- Example: Setting aside contingency funds for potential cost overruns.
-
Contingency Planning:
- Technique: Develop specific actions to take if the risk materializes.
- Example: Creating a backup plan for critical project tasks.
Example Matrix:
| Low Impact | Medium Impact | High Impact | |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Likelihood | R1 | R2 | R3 |
| Medium Likelihood | R4 | R5 | R6 |
| Low Likelihood | R7 | R8 | R9 |
Creating a Probability and Impact Matrix
What is a Probability and Impact Matrix?
A Probability and Impact Matrix, also known as a Risk Matrix or Risk Assessment Matrix, is a visual tool that aids project managers in prioritizing risks based on their likelihood of occurrence and potential impact. The matrix facilitates a structured and data-driven approach to risk management.
Constructing the Matrix
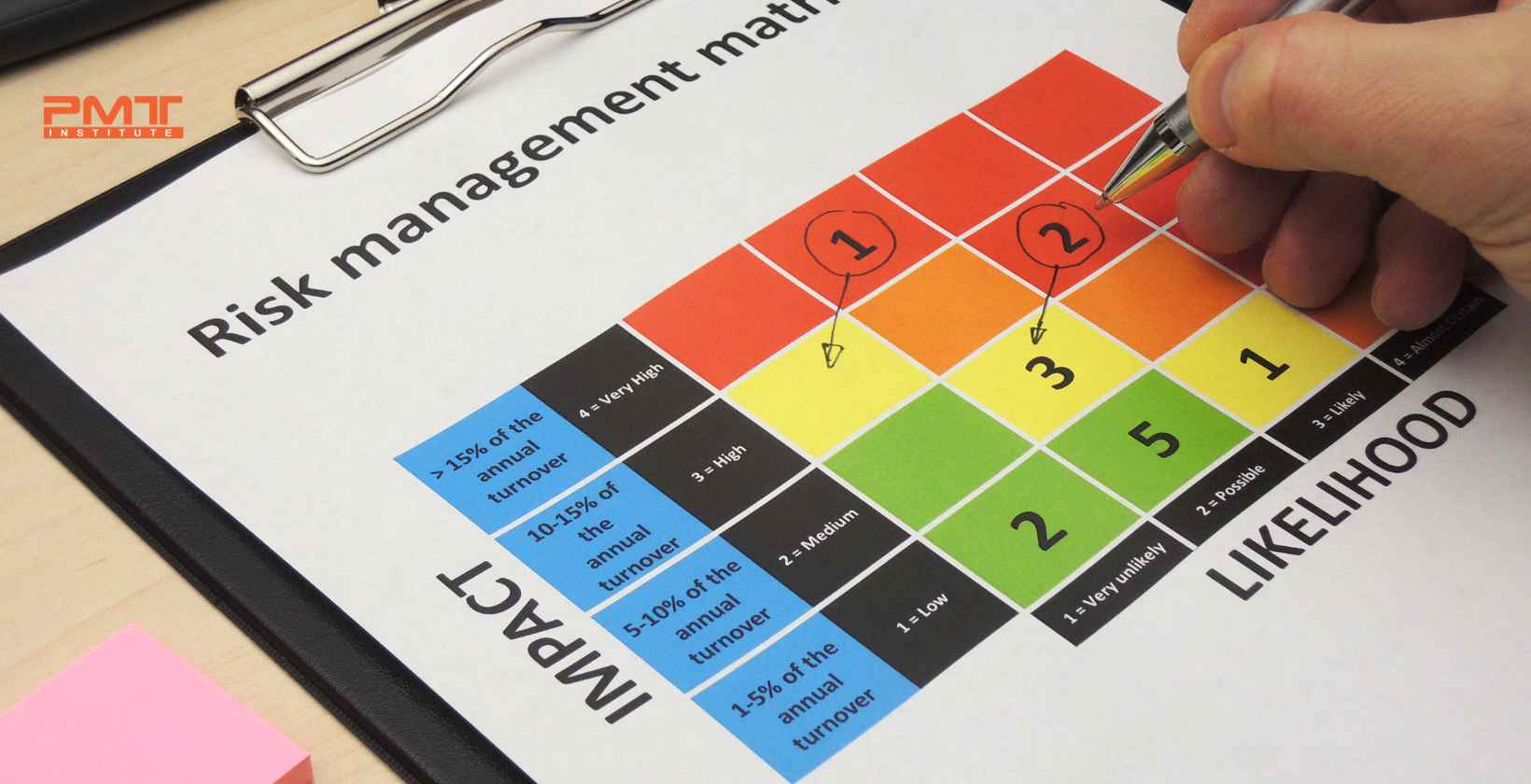
To create a Probability and Impact Matrix, project managers follow these steps:
Using the Probability and Impact Matrix
Risk Prioritization
The Probability and Impact Matrix enables project managers to prioritize risks effectively:
Risk Mitigation Strategies
To effectively manage identified risks, project managers must develop appropriate risk responses for each risk, including preventive measures to reduce probability and mitigative actions to minimize impact. Adequate resource allocation and clearly defined responsibilities are crucial for successful risk management.
Risk mitigation strategies are essential for minimizing the impact and likelihood of risks. They involve strategic planning and actions to reduce potential threats to project success.
Techniques and Examples
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Mitigation Strategies
Regular evaluation of risk mitigation strategies is crucial to ensure they are effective and adapt to changing project conditions.
Updating the Matrix
Dynamic Nature of Risks
Projects evolve over time, and risks may emerge or change throughout the project lifecycle. It is essential to recognize the dynamic nature of risks and anticipate potential alterations in the risk landscape.
Regular Review and Reassessment
To ensure the Probability and Impact Matrix remains accurate and relevant, project teams must schedule periodic risk reviews. Incorporating new data, feedback from stakeholders, and lessons learned from previous projects will contribute to effective risk management.
Final Thoughts
Risk probability, impact assessment, and the probability and impact matrix are indispensable tools for project managers seeking to enhance project success and minimize potential threats. By accurately understanding the likelihood and consequences of risks, project teams can make informed decisions and implement appropriate mitigation strategies.
Creating a solid Probability and Impact Matrix is a critical step in effective PMP risk management. Identifying and prioritizing risks can help project managers anticipate potential challenges and mitigate their impacts.
This proactive approach not only enhances the likelihood of project success but also ensures that resources are allocated efficiently and stakeholders remain confident in the project's direction.


