Matrix Diagrams in Project Management
Published:
Updated:
Project managers often face the challenge of managing multiple people, processes, and tasks simultaneously. One essential tool to simplify this complexity is the matrix diagram. Matrix diagrams help visualize and analyze complex relationships, enabling project managers to make informed decisions. In this blog, we'll explore matrix diagrams, their uses in project management, and how they are tested in the PMP exam.
Key Takeaways
- Matrix Diagrams Visualize Relationships: Matrix diagrams help project managers identify and analyze relationships between different sets of data, making them essential for decision-making and problem-solving.
- Types of Matrix Diagrams: There are five key types of matrix diagrams: L-shaped, Y-shaped, C-shaped, T-shaped, and X-shaped, each suited for different project scenarios.
- Relevance to PMP Exam: Matrix diagrams are vital tools in project management and are tested in the PMP exam, helping with tasks such as resource allocation, risk management, and team assignments.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By clearly mapping the relationships between tasks, people, and resources, matrix diagrams allow project managers to make more informed decisions and improve project outcomes.
- Common Applications: Matrix diagrams are commonly used for resource allocation, problem identification, risk management, and comparing potential solutions, making them versatile tools in various industries.
- Practical Tools for Matrix Diagrams: Tools like MS Excel, Lucidchart, Miro, and SmartDraw simplify the creation of matrix diagrams, allowing project managers to efficiently visualize data relationships.
- Best Practices for Using Matrix Diagrams: Start with simple relationships, involve team members for better accuracy, and update the matrix regularly to ensure it stays relevant throughout the project lifecycle.
- Challenges to Consider: While matrix diagrams are valuable, they can be time-consuming and complex if not managed well, especially when dealing with large data sets.
Matrix diagrams are an essential tool for project managers, helping them understand complex relationships and make data-driven decisions that lead to better project execution and risk management.
What is a Matrix Diagram?
A matrix diagram is a project management tool that helps understand and analyze relationships between different sets of data. It allows project managers to compare elements across multiple groups and visualize the connections, helping to determine how data sets interact and the strength of these interactions.
A matrix can represent the relationship between data sets like:
- Tasks
- People
- Resources
- Equipment
- Functions
- Concepts
Typically, symbols or numbers indicate relationships in the matrix cells, showing the strength of the connections between elements. Depending on the number of elements being compared, there are various types of matrix diagrams to choose from.
Types of Matrix Diagrams
Matrix diagrams come in different forms, each tailored to specific project management needs. Here are the five main types of matrix diagrams:
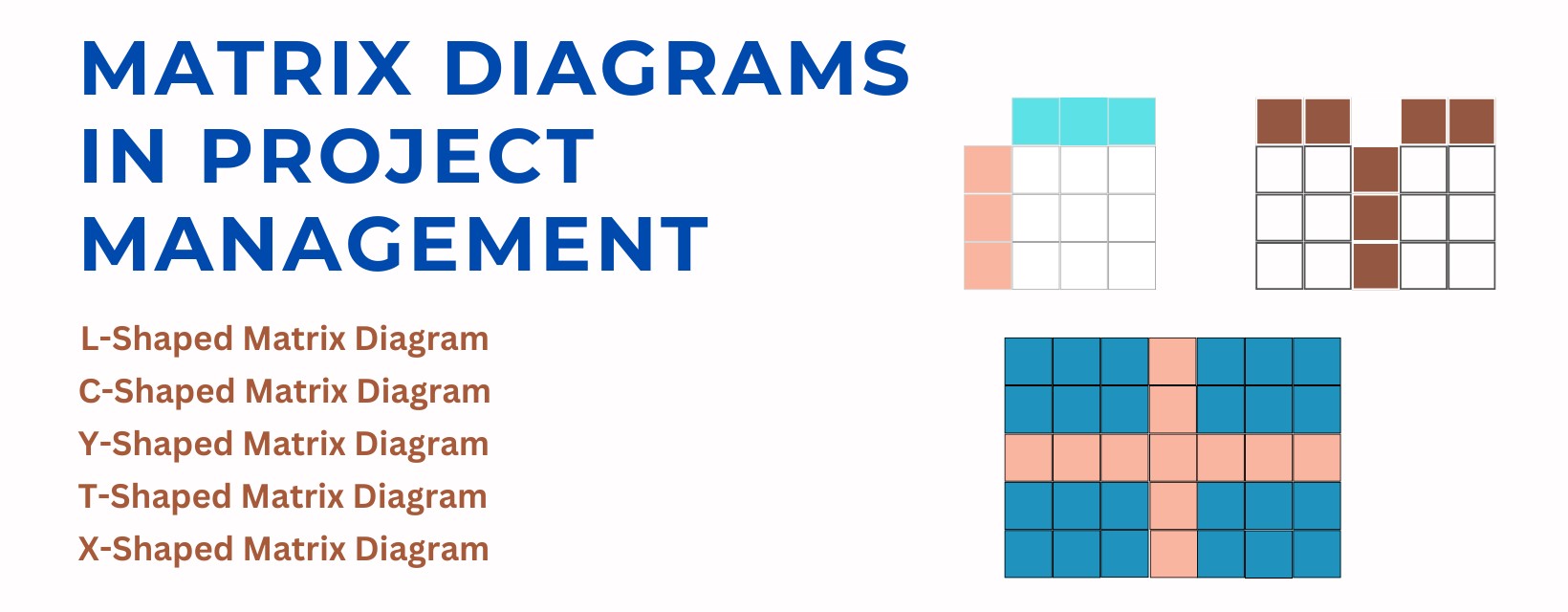
- L-Shaped Matrix Diagram:
What it is: This is the most common matrix type and compares two sets of data in a two-dimensional table. Symbols or numbers are used to indicate the relationship between the elements in the intersecting cells.
When to use: Ideal for comparing two groups of items (e.g., tasks vs. resources). - Y-Shaped Matrix Diagram:
What it is: This matrix type connects three groups of related elements in a circular flow, showing relationships between all three.
When to use: Useful when comparing three closely related groups, such as goals, resources, and constraints. - C-Shaped Matrix Diagram:
What it is: Similar to the Y-shaped matrix, this diagram compares three sets of data but in a three-dimensional format.
When to use: Great for comparing groups such as products, people, and processes in a single analysis. - T-Shaped Matrix Diagram:
What it is: A T-shaped matrix links one central data set to two others, making it a hybrid of two L-shaped matrices.
When to use: Best for scenarios where two groups of elements are related to a common core set, but not necessarily to each other. - X-Shaped Matrix Diagram:
What it is: An X-shaped matrix compares four sets of data, each related to the group next to it but not directly across.
When to use: Use this when analyzing four distinct data groups that are indirectly related (e.g., products, teams, timelines, and risks).
Matrix Diagrams in the PMP Exam Context
Understanding matrix diagrams is essential for PMP certification aspirants. In project management, matrix diagrams play a vital role in decision-making and resource allocation. The PMP exam may test your ability to:
- Interpret matrix diagrams for project planning.
- Use matrix analysis to decide on resource assignments, roles, and relationships.
- Analyze the impact of interconnected variables on project outcomes.
For example, matrix diagrams can assist in identifying relationships between project stakeholders, ensuring resources are effectively allocated, and aligning tasks with the appropriate team members.
Why Use Matrix Diagrams in Project Management?
Matrix diagrams are invaluable for project managers because they:
- Simplify complex relationships: When multiple variables interact, a matrix diagram helps visualize these connections clearly.
- Improve decision-making: By mapping relationships, project managers can make better-informed decisions on resources, timelines, and responsibilities.
- Highlight dependencies: Matrix diagrams show how tasks, people, or processes depend on each other, ensuring better coordination and risk mitigation.
- Enhance communication: These visual tools make it easier to present data to stakeholders and team members, leading to better understanding and collaboration.
When to Use Matrix Diagrams
Matrix diagrams should be used when project managers need to:
- Identify problem areas.
- Allocate resources based on need or competency.
- Compare potential solutions.
- Identify improvement opportunities.
- Assess relationships during a Quality Function Deployment (QFD) analysis.
How to Create a Matrix Diagram
Here's a step-by-step guide to creating a matrix diagram:
- Define Your Purpose: Clarify the goal of the matrix diagram—whether it's to make a decision, analyze relationships, or prioritize tasks.
- Assemble Your Team: Gather a team with relevant expertise to help analyze the data sets and interpret the relationships.
- Collect Data Sets: Identify and gather the data that will be used for the analysis.
- Choose the Right Matrix Type: Select the appropriate matrix type based on the complexity and nature of the data.
- Compare Data: Decide on the criteria for comparing data, and choose symbols or numbers to represent relationships.
- Document Relationships: Go through each cell, noting the strength of the relationship between elements.
- Analyze Results: After completing the matrix, review the data and draw conclusions to guide your project decisions.
Example of Matrix Diagrams in Action
Here are two examples of matrix diagrams commonly used in project management:
Task Assignment Matrix
| Task | Team Member 1 | Team Member 2 | Team Member 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Task 1 | X | ||
| Task 2 | X | ||
| Task 3 | X | ||
| Task 4 | X | X | |
| Task 5 | X | X |
This matrix helps track task assignments and ensures clarity on who is responsible for each task.
Risk Management Matrix
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk 1 | High | High | High |
| Risk 2 | Medium | Low | Medium |
| Risk 3 | Low | Medium | Medium |
| Risk 4 | High | Low | Low |
This risk matrix helps prioritize potential risks, focusing on high-priority risks first.
Benefits of Using Matrix Diagrams
Matrix diagrams offer several key advantages that make them indispensable in project management. These benefits help project managers in organizing complex information, improving decision-making, and enhancing collaboration.
- Enhanced Decision-Making
Matrix diagrams enable project managers to see relationships and dependencies between different variables. This clear visualization aids in making informed, data-driven decisions that account for multiple factors at once, ensuring a more comprehensive analysis. - Improved Communication
A matrix diagram simplifies complex data into a visual format that is easier for teams and stakeholders to understand. It can be used during meetings or presentations to clearly show how tasks, resources, or risks are interrelated, improving overall project communication and collaboration. - Clarity in Resource Allocation
Project managers often juggle many resources across multiple tasks. Matrix diagrams provide a clear way to allocate resources effectively by mapping responsibilities and ensuring that each task has the necessary support without overloading team members. - Risk Identification
One of the major benefits of using matrix diagrams is the ability to identify risks early on. By mapping out how various elements of the project interact, project managers can pinpoint areas of potential risk or bottlenecks that need attention.
Challenges of Using Matrix Diagrams
While matrix diagrams are a powerful tool, they are not without their challenges. Understanding these challenges can help project managers use the tool more effectively and avoid potential pitfalls.
- Time-Consuming
Creating a detailed matrix diagram requires a significant investment of time, especially for large projects with many variables. The process of collecting and organizing data, choosing the right matrix type, and completing the diagram can slow down project planning if not managed properly. - Complexity
As the project grows in size and scope, the matrix diagram can become increasingly complex. Managing large datasets with multiple interconnections can make the matrix difficult to read or interpret, which can reduce its effectiveness as a decision-making tool. - Data Overload
Matrix diagrams are most effective when focused on key data sets. Including too many variables in one matrix can lead to data overload, where the diagram becomes cluttered and overwhelming. It is essential to keep the diagram focused on the most relevant information to avoid confusion. - Stakeholder Misunderstanding
For stakeholders unfamiliar with matrix diagrams, the representation of relationships in rows and columns may not be immediately intuitive. This could lead to miscommunication or misinterpretation of the data if not clearly explained.
Best Practices for Using Matrix Diagrams
To maximize the benefits of matrix diagrams, it's important to follow some best practices that ensure the diagrams remain clear, effective, and actionable.
- Start Simple
Begin by focusing on the most critical data sets or relationships. As the project progresses, you can gradually introduce additional layers of complexity. This prevents data overload and ensures the diagram remains easy to interpret. - Involve Your Team
Collaborative matrix diagram creation ensures that all team members understand the relationships and dependencies within the project. It also ensures that the data included in the diagram is accurate and represents multiple perspectives. - Regular Updates
Matrix diagrams should not be static. As the project evolves, new relationships and risks may emerge. Regularly update the matrix to reflect the current project status, ensuring that it remains a relevant tool for decision-making. - Use Symbols and Scoring
Use standardized symbols (e.g., circles, squares) or a scoring system to indicate the strength of relationships in the matrix. For instance, you can use a 1-5 scale to rate the strength of a relationship between tasks or resources, making the diagram even more informative. - Keep Documentation
Document the rationale behind each relationship or data point in the matrix. This provides context and transparency, especially if the matrix is referenced later in the project lifecycle.
Tools for Creating Matrix Diagrams
Several tools and software solutions make it easy to create matrix diagrams. Using the right tool can save time and increase accuracy in data presentation.
- MS Excel
Excel is widely used in project management and offers customizable options to create basic matrix diagrams. You can set up rows and columns, apply formulas, and use conditional formatting to highlight key relationships. - Lucidchart
Lucidchart is an online diagramming tool that simplifies the process of creating various types of matrix diagrams. It offers pre-built templates, making it easy for project managers to customize and share diagrams with their teams. - Miro
Miro is an online collaboration tool that allows teams to build and share matrix diagrams in real-time. It's particularly useful for remote teams or those needing frequent updates to their diagrams. - SmartDraw
SmartDraw is a versatile diagramming tool that supports matrix charts and other project management diagrams like Gantt charts and flowcharts. It offers a variety of templates, enabling quick creation of matrix diagrams with minimal effort.
Real-World Case Study
Matrix diagrams have been successfully used in various industries and project scenarios. Below is an example of how a matrix diagram can be implemented in the real world.
Case Study: Risk Management in Construction
In a large construction project, the project management team was faced with the challenge of managing multiple subcontractors, each responsible for different tasks like plumbing, electrical work, and carpentry. The team created a risk management matrix to monitor potential risks associated with each subcontractor's performance.
The matrix included columns for tasks (e.g., electrical wiring, foundation work), potential risks (e.g., delays, safety issues), likelihood of risk (e.g., high, medium, low), and impact (e.g., high, medium, low). This matrix allowed the team to prioritize risks and allocate resources where they were needed most, mitigating potential delays and cost overruns.
Outcome
The matrix helped the project team anticipate problems, communicate risks to stakeholders, and focus on high-priority issues. As a result, the project was completed on time and within budget, demonstrating the power of using matrix diagrams for risk management.
Conclusion
Matrix diagrams are essential tools for project managers, allowing them to better understand the relationships between different project elements and make data-driven decisions. Whether you're preparing for the PMP exam or managing a complex project, matrix diagrams can help visualize complex data and improve project outcomes.
By mastering matrix diagrams, project managers can better allocate resources, assess risk, and ensure project success.


